Feeling stuck with a Windows issue? You’re not alone. Knowing exactly how to get help in windows can be frustrating, but thankfully, Microsoft has built-in powerful tools to guide you.
This article will show you every method, from simple keyboard shortcuts to hidden gems that will make solving problems a breeze.
- Connect Your Problem to the Right Solution
- How to Get Help in Windows 11/10
- Windows Troubleshooting Tools
- 5. Run a Windows Troubleshooter
- 6. Leveraging Windows Update & Security for Proactive Help
- 7. Use the Steps Recorder to Show Your Problem (Unique Method)
- 8. Check the Event Viewer for Clues
- 9. View the Reliability Monitor for an Easy Diagnosis (Unique Method)
- 10. Run a System File Checker (SFC) Scan and DISM
- Built-in Guidance Apps
- Search and Remote Assistance
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion: You’re Now Ready to Solve Any Problem
Dealing with a computer problem can bring your productivity to a halt. Fortunately, whether you’re using Windows 10 or Windows 11, there are numerous ways to find the solutions you need directly within the operating system. Let’s dive into each method, step-by-step.
Connect Your Problem to the Right Solution
Before you start, here’s a quick guide to match your problem with the best tool:
- For Printer, Wi-Fi, or Sound issues: Start with the Windows Troubleshooter (Method 4).
- For a specific app error: Press the F1 Key while in the app (Method 3).
- If you need to show someone your exact issue: Use the Steps Recorder (Method 8).
- If your PC is suddenly slow or crashing: Check the Reliability Monitor (Method 14) or run an SFC Scan (Method 15).
How to Get Help in Windows 11/10
1. Use the Built-in ‘Get Help’ Application
First and foremost, your primary tool is the dedicated “Get Help” app. It’s a powerful resource that uses an AI chatbot to understand your issue and can even connect you with a human agent if needed.
Click the Start Menu button.
Type ‘Get Help’ into the search bar, then click on ‘Open‘.
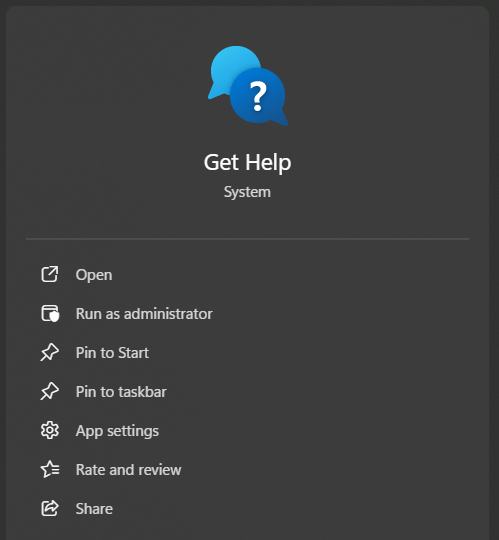
In the app window that opens, type your question or describe your problem in plain language (e.g., “Bluetooth speaker not connecting” or “screen flickering”).
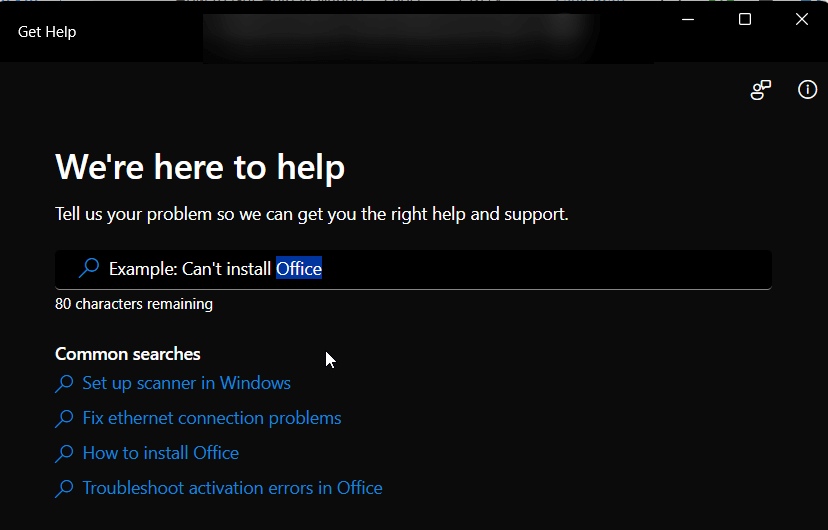
Follow the on-screen prompts. If the issue isn’t resolved, the app will often provide an option to ‘Contact Support’.
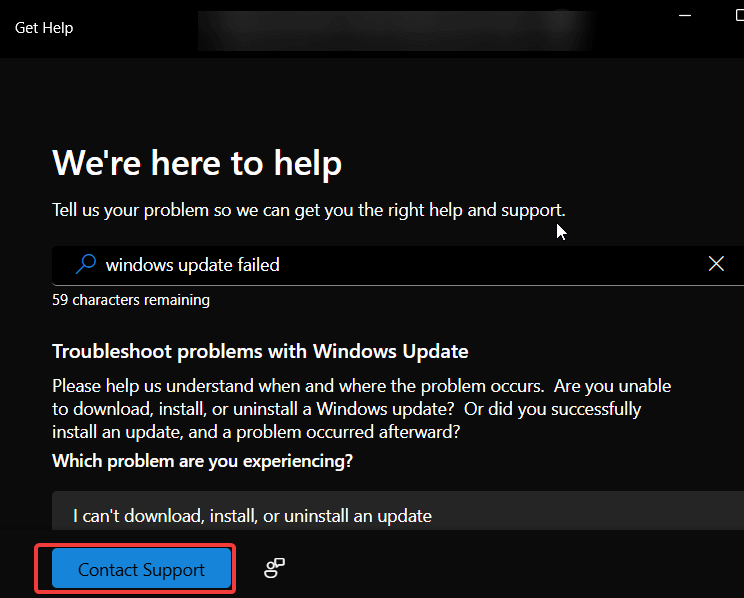
2. Use Live Chat or Request a Phone Call
If the automated solutions aren’t enough, you can often reach out to a human support agent directly through various Microsoft channels.
Via the Get Help App (Continued):
After describing your issue in the Get Help app (see Method 1), if you click Contact Support, you’ll usually be asked to confirm your product (e.g., Windows) and category of the issue (e.g., Technical support).
Once confirmed, you’ll often see options like:
- Chat with a support agent in your web browser: This will open a live chat session.
- Global Customer Service Phone Numbers: Schedule a callback.
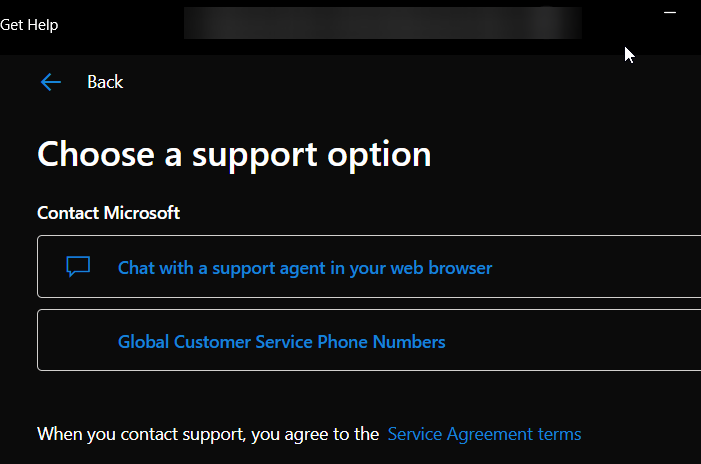
Choose your preferred method and follow the prompts. You may need to sign in with your Microsoft account.
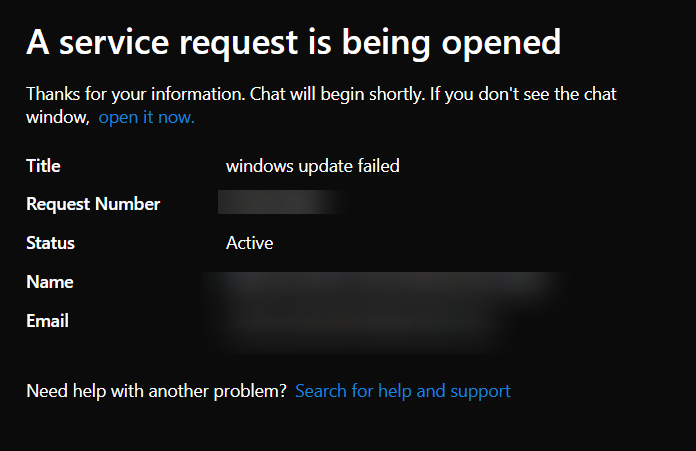
It will create Service Ticket to the support before connecting you to the agent. Once created, click link “open it now” to open the chat.
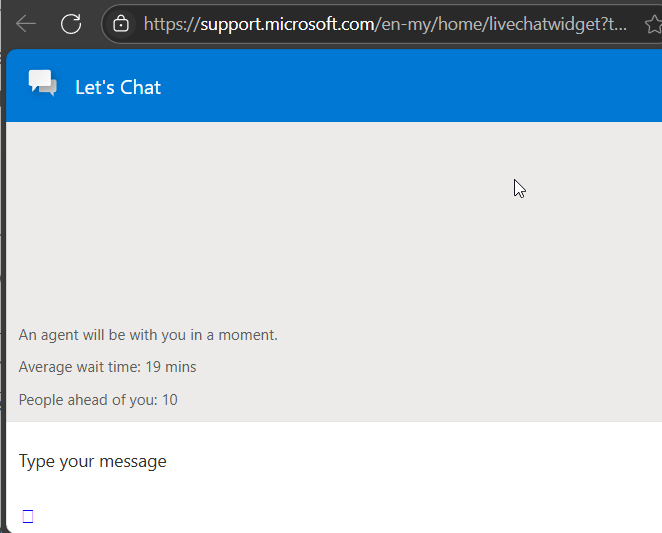
Once the live chat is open, you can start to ask your question.
Via the Microsoft Support Website (for business users or alternative access):
Microsoft provides Global Customer Service phone numbers for support, especially useful for business users or if the app isn’t working. You can find these on the Microsoft Support website.
3. Press the F1 Key for Instant Help
The F1 key is a classic Windows shortcut for help that still works in many applications. It provides context-sensitive help related to the window you currently have open.
This will typically open:
- A dedicated help window for that application.
- The Windows Get Help app.
- A web browser directed to an online help page relevant to the application or context.
While its function can vary, it’s always worth a quick press to see if it provides the specific help you need for the task at hand.
4. Browse the Official Microsoft Support Website
The official Microsoft Support website is a comprehensive hub for documentation, tutorials, and direct support options.
To find help on Microsoft Support, open your web browser and go to https://support.microsoft.com/windows.
Use the prominent search bar on the page to type your query, error message, or the feature you need help with.
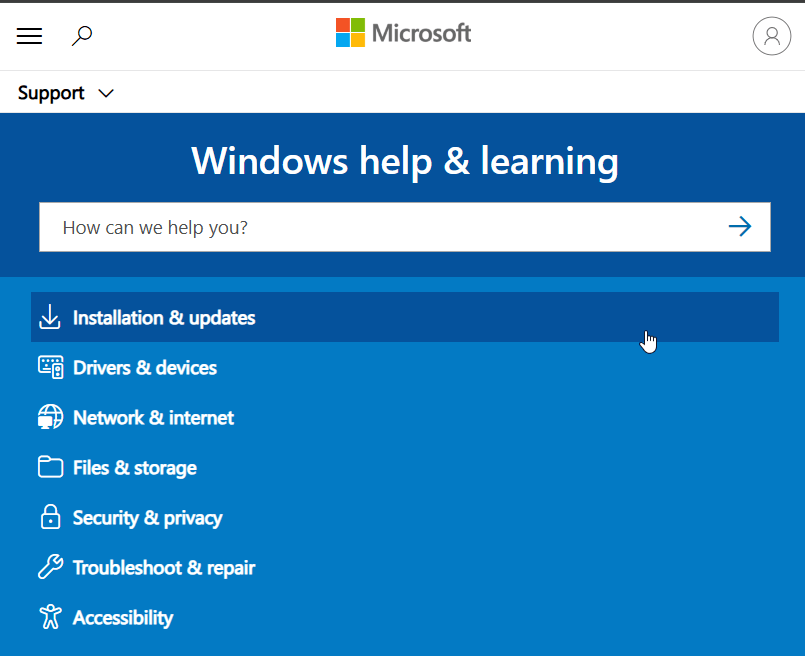
Browse the search results for official Microsoft articles, troubleshooting guides, and how-to’s.
Alternatively, you can browse by category (e.g., Installation & updates, Security & privacy, Drivers & devices).
This is an excellent resource for official documentation and validated solutions.
Windows Troubleshooting Tools
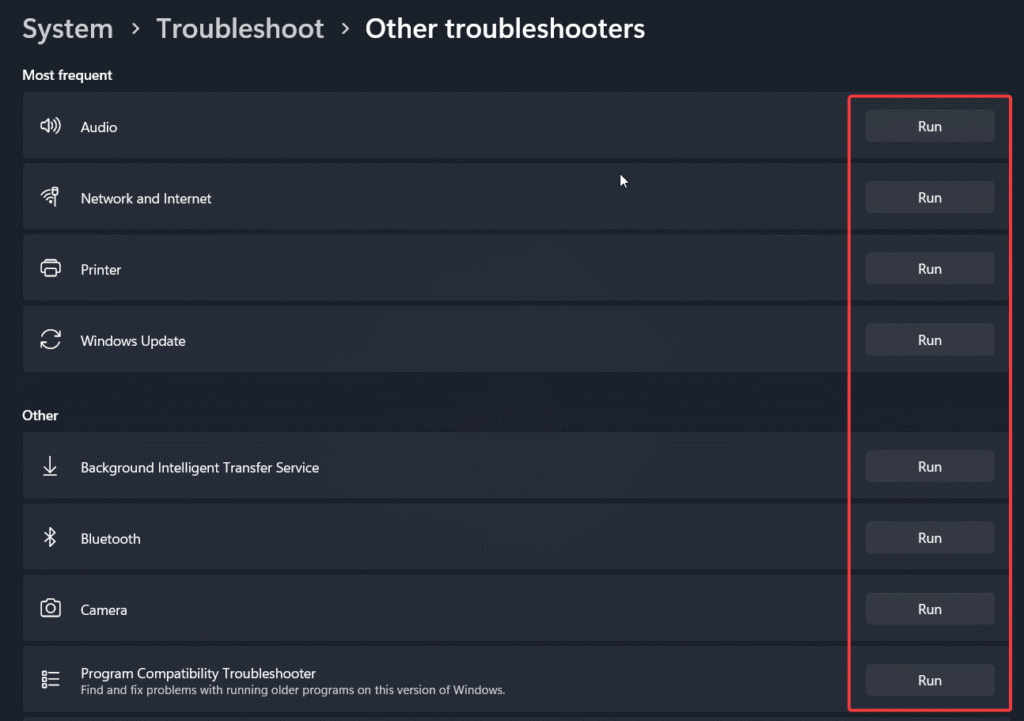
5. Run a Windows Troubleshooter
Next, Windows has a suite of built-in troubleshooters designed to automatically find and fix common issues with networking, audio, printers, and more.
How to Find and Run a Troubleshooter:
Right-click the Start Menu and select Settings.
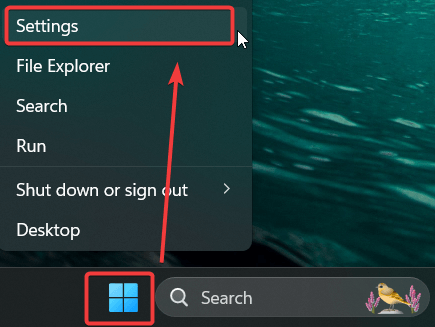
Navigate to System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters.
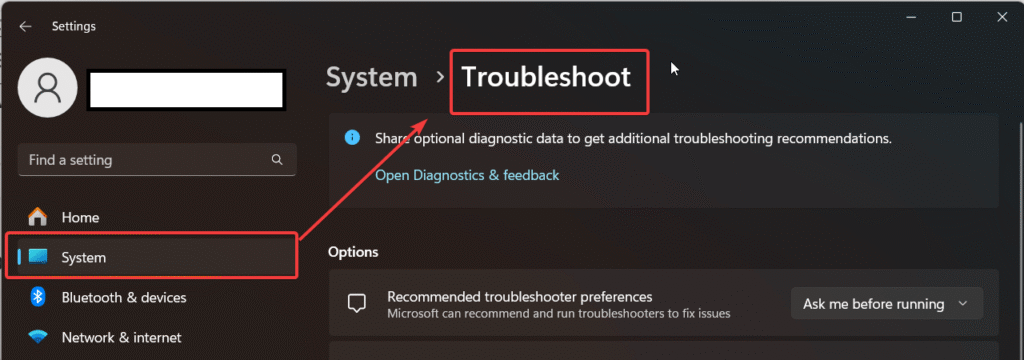
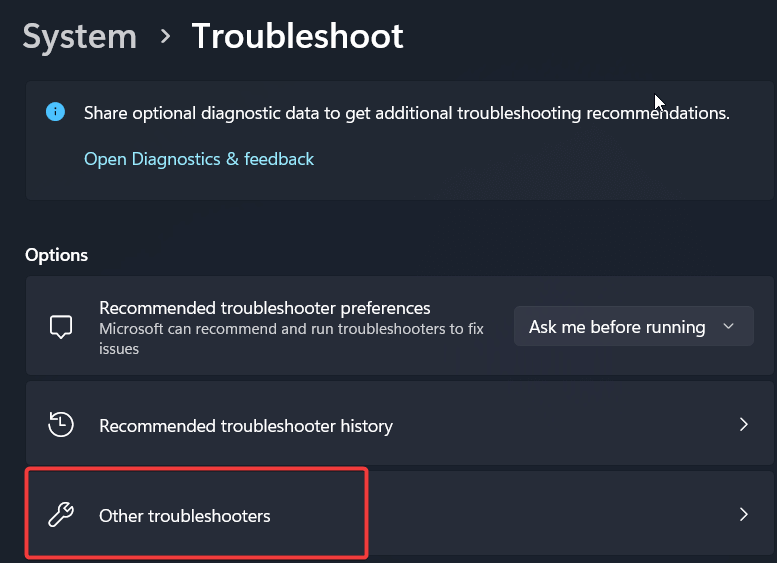
Find the troubleshooter relevant to your issue and click Run.
6. Leveraging Windows Update & Security for Proactive Help
One of the best ways to get help is to prevent problems. Windows Update and Windows Security are your first line of defense.
- Windows Update: Regularly installing updates can fix known bugs and patch security holes.
- Windows Security: Run a regular virus scan to ensure malware isn’t causing problems.
7. Use the Steps Recorder to Show Your Problem (Unique Method)
Struggling to describe a complex problem? Let Windows show it for you. The Steps Recorder is a little-known tool that records your mouse clicks as a series of annotated screenshots.
How to Use the Steps Recorder:
In the Start Menu, search for ‘Steps Recorder’ and open it.

Click Start Record.

Perform the actions that are causing the error.
Click Stop Record. It will show a recorded every action you did during recording.

If you want to save it (like you need to attach in support ticket), click Save.

It will save in zip format, where the inside the zip file is the recorded steps, in .mht file format.

Once open the .mht file, you can find the recorded steps earlier.

8. Check the Event Viewer for Clues
For advanced users, the Event Viewer logs significant events on your computer, providing error codes and details for diagnosing crashes.

9. View the Reliability Monitor for an Easy Diagnosis (Unique Method)
If the Event Viewer is too technical, use the Reliability Monitor instead. It offers a simple, visual timeline of your PC’s health and stability.
How to Access the Reliability Monitor:
In the Start Menu, search for ‘Reliability Monitor’ and open it.

You will see a graph of your system’s stability. Red “X” icons indicate critical events. Clicking on any day will show you exactly what apps failed or what updates were installed.
10. Run a System File Checker (SFC) Scan and DISM
If you suspect core Windows files are corrupted, the SFC utility can scan and restore them.
How to Run an SFC Scan:
Search for ‘Command Prompt’, right-click it, and select Run as administrator.
Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
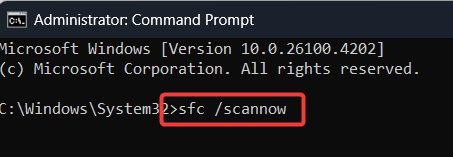
Let the scan complete. It will attempt to repair any corrupt files it finds.
How to Run an DISM Scan
Deployment Image Servicing and Management(DISM) can repair the Windows system image, which SFC uses as a reference.
Open Command Prompt as administrator
Run these commands one by one:
- DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth
- DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealthDISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
These tools can resolve deeper system stability problems but should be used with understanding.
Built-in Guidance Apps
11. Leverage the “Tips” App for Guidance
The “Tips” app provides short, easy-to-follow guides on how to use various Windows features. Simply search for “Tips” in the Start Menu to open it.
Browse through categories like “What’s new,” “Personalization,” “Productivity,” or use the search within the Tips app to find specific information.
The Microsoft Tips app is great for discovering new functionalities and keyboard shortcuts.
12. Use the “Get Started” App (Windows 11)
For Windows 11 users, the “Get Started” app is a fantastic introduction that walks you through new features and helps you set up your PC.
If you’re new to Windows or want to explore its features, the “Get Started” app provides a guided introduction.
Click the Search icon on your taskbar, then type Get Started and select the app from the results.
The app will walk you through setting up your experience, personalizing Windows, and learning about key features like the Start menu, File Explorer, and Microsoft Edge.
This app is particularly helpful for users transitioning to a new version of Windows.
13. A Note on Accessibility: Foundational Help for All Users (Unique Angle)
Sometimes, the help you need is simply being able to interact with your computer more easily. Windows has a full suite of accessibility tools to help with this.
- Search for ‘Ease of Access’ in Settings to find tools like:
- Narrator: A screen reader that reads text and buttons aloud.
- Magnifier: A tool to enlarge parts of your screen.
- High Contrast: Themes that make text easier to read.
Search and Remote Assistance
14. Use Quick Assist for Remote Help
If you need help from a friend or IT professional, Quick Assist allows someone you trust to securely control your computer remotely to fix the problem for you.
Search for Quick Assist in the Windows search bar and open the app.

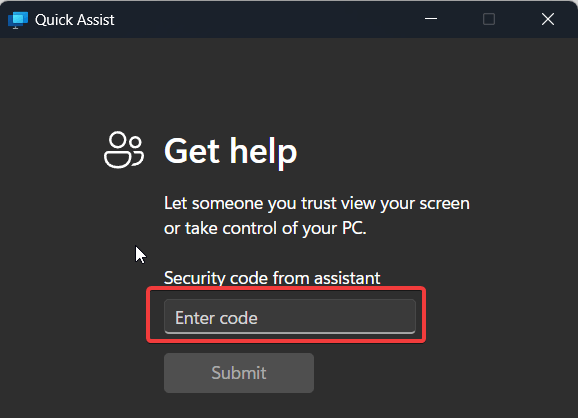
If you are getting help:
- The person assisting you will provide a 6-digit security code.
- Enter this code under “Get assistance” in your Quick Assist window and click Submit.
- You will then be prompted to Allow them to take full control or view your screen.
If you are giving help:
- Click Assist another person.
- Sign in with your Microsoft account if prompted.
- A security code will be generated. Share this code with the person you are assisting.
- Once they enter the code, you’ll be able to choose between Take full control or View screen.
Both users need a stable internet connection for Quick Assist to work effectively.
15. Search Your Problem in the Start Menu
Don’t underestimate the power of the Windows search bar. Type your question directly into it to get settings recommendations and web results from Bing.
16. Explore the Microsoft Community Forums
The Microsoft Community is a massive forum where you can post questions and get answers from fellow users and Microsoft MVPs.
Go to answers.microsoft.com.
You can search for existing questions that match your problem.
If you can’t find a solution, you can sign in with your Microsoft account and post your own question, providing as much detail as possible about your issue and your system.
17. Consult Third-Party Resources
Finally, remember that help exists outside of Microsoft’s ecosystem. Reputable tech sites, forums like Reddit (such as the r/WindowsHelp subreddit), and YouTube channels are excellent sources for detailed guides.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the keyboard shortcut for help in Windows?
A: The universal shortcut is the F1 key.
Q: How can I get help from a real person at Microsoft?
A: The best way is to use the Get Help app, which can connect you to a live agent via chat.
Q: What is the easiest way to show someone my computer problem?
A: Use the built-in Steps Recorder. It automatically creates a step-by-step document with screenshots that you can easily share.
Conclusion: You’re Now Ready to Solve Any Problem
As you can see, Windows is packed with powerful tools to help you resolve nearly any issue. From the simple F1 key and proactive security scans to unique hidden gems like the Reliability Monitor and Steps Recorder, you are never truly on your own.
Bookmark this guide for future reference. The next time you face a challenge, you’ll know exactly where to turn.
Which of these methods have you found most helpful? Share your experiences in the comments below or share this post with someone who might need it.
IT Security / Cyber Security Experts.
Technology Enthusiasm.
Love to read, test and write about IT, Cyber Security and Technology.
The Geek coming from the things I love and how I look.