Feeling frustrated by software that crashes, freezes, or just won’t work? You’re not alone. This guide will teach you how to troubleshoot software issues with a simple, repeatable methodology. Say goodbye to guesswork and hello to effective, confident problem-solving that gets you back to work fast.
- The Troubleshooter’s Mindset: A Note on Patience and Logic
- How to Troubleshoot Software Issues : 3 Quick Fixes to Try First (And Why They Work)
- The Universal 7-Step Software Troubleshooting Methodology
- Step 1: Identify the Exact Problem (Gather Information)
- Step 2: Recreate the Problem Consistently
- Step 3: Isolate the Cause (Form a Hypothesis)
- Step 4: Test Your Hypothesis
- Step 5: Implement the Solution
- Step 6: Verify the Fix and Check for Side Effects
- Step 7: Document the Process (Prevent Future Issues)
- Leveraging Community Knowledge: You’re Not Alone
- 12 Common Software Issues and Their Specific Fixes
- Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques for Tough Problems
- Helpful Tools for Software Troubleshooting
- Best Practices for Preventing Software Problems
- When to Stop: Knowing When to Call for Professional Help
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion: You Are Now the Troubleshooter
The Troubleshooter’s Mindset: A Note on Patience and Logic
Before you touch a single setting, take a deep breath. The most powerful troubleshooting tool is a calm and logical mind. Frustration leads to random clicking, which can make the problem worse.
Instead, adopt the mindset of a detective: your goal is to gather clues, form a theory, and test it methodically. Patience will solve the problem faster than panic.
How to Troubleshoot Software Issues : 3 Quick Fixes to Try First (And Why They Work)
Before diving into a deep diagnosis, it’s amazing how often the simplest solutions work. When a problem first appears, save yourself time and start with these three quick fixes.
- Restart the Application.
- Why it works: This simple step clears the application’s temporary cache and resets its current state, resolving minor glitches or memory leaks that occurred while it was running.
- Check for Updates.
- Why it works: Developers constantly release updates (patches) to fix known bugs. The issue you are facing might be a widely reported problem that has already been solved in the latest version.
- Reboot the Computer.
- Why it works: A full reboot clears your computer’s entire volatile memory (RAM) and terminates all background processes, some of which may have been stuck or conflicting with your software. It provides a completely clean slate.
The Universal 7-Step Software Troubleshooting Methodology
If the quick fixes didn’t solve your problem, it’s time to move from guessing to a structured process. This is the same systematic approach that IT professionals use to diagnose and resolve issues efficiently.
By following these steps on how to troubleshoot software issues, you can tackle nearly any software problem with confidence.
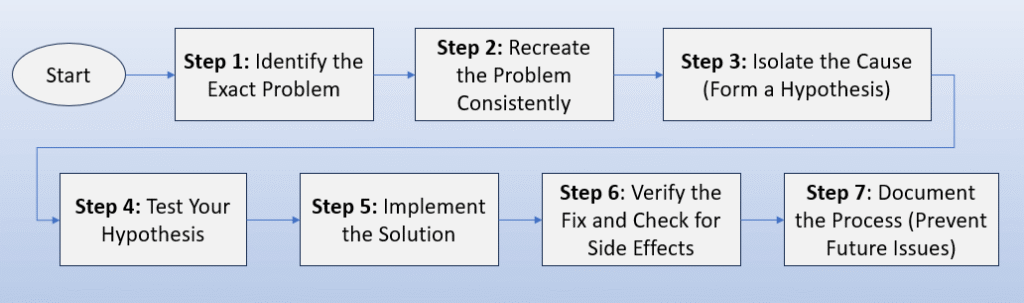
Step 1: Identify the Exact Problem (Gather Information)
First, you need to stop and observe. What is actually happening? Instead of just saying “it’s broken,” ask specific questions:
- What are the exact symptoms? Is the program slow, freezing, or showing an error message?
- Is there a specific error message? If so, write it down or take a screenshot. That code is your biggest clue.
- Is the problem affecting the entire program or just one specific feature?
Step 2: Recreate the Problem Consistently
Next, can you make the problem happen again on purpose? A consistent, repeatable problem is much easier to solve. Document the exact sequence of clicks and actions that triggers the issue. For instance, “The program crashes every time I click File, then Export.”
Step 3: Isolate the Cause (Form a Hypothesis)
With the information you’ve gathered, you can now form an educated guess, or hypothesis. Think about what might have changed recently. Did you just install a new program? Did you update a driver? Common causes include:
- A recent software or OS update.
- Conflicts with other software (like an antivirus program).
- Corrupted files.
- The software not meeting your computer’s system requirements.
Step 4: Test Your Hypothesis
Now, test your guess by changing only one variable at a time. If you think a new plugin is the cause, disable only that plugin and try to recreate the problem.
If you suspect an antivirus conflict, temporarily disable the antivirus and test again. Changing one thing at a time is crucial; otherwise, you won’t know which change was the actual fix.
Step 5: Implement the Solution
Once you have confirmed your hypothesis, apply the permanent fix. This could mean rolling back a problematic driver, uninstalling conflicting software, or reinstalling the corrupted program.
Step 6: Verify the Fix and Check for Side Effects
After applying the solution, thoroughly test the software. First, confirm that the original problem is gone. Second, check other core features of the program to ensure your fix hasn’t accidentally caused a new problem elsewhere.
Step 7: Document the Process (Prevent Future Issues)
Finally, take a quick note of the problem and the solution. This simple step can save you hours of work if the issue ever reappears. It also helps you recognize patterns over time, making you a more effective troubleshooter.
Leveraging Community Knowledge: You’re Not Alone
When an error message is cryptic or a problem is unique, remember this: someone else has probably faced it before. Tapping into collective user experience is a pro-level skill.
- Be a Better Searcher: Instead of just Googling the program name, search the full, exact error message in quotes (e.g., “unexpected kernel mode trap”).
- Use Specific Forums: The best help often comes from dedicated communities. Check the software’s official support forums, or specialized communities like Reddit’s r/techsupport or the relevant Stack Exchange site. These are goldmines of expert and user-submitted solutions.
12 Common Software Issues and Their Specific Fixes
Here’s a breakdown of some of the most frequent software headaches and how to troubleshoot software those issues using our methodology.
Pro-Tip: Before attempting a fix like a reinstall, always back up your important data and settings associated with the application.
- The Software is Running Extremely Slow.
- Fix: Check your computer’s Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc on Windows) or Activity Monitor (on Mac) to see if the program is using too much CPU or RAM. Close other unnecessary background applications.
- The Application Keeps Crashing or Freezing.
- Fix: This often points to a compatibility issue or corrupted files. Ensure the software and your drivers are up to date. If that fails, a complete reinstall of the application is the next logical step.
- Problems During Software Installation.
- Fix: First, confirm your computer meets the minimum system requirements. Try running the installer as an administrator (right-click and select “Run as administrator“). Temporarily disabling your antivirus during installation can also help.
- Error Messages on Startup or During Use.
- Fix: Don’t ignore the message! Type the exact error code or message into Google. You will almost certainly find a forum or support document from someone who has solved the exact same issue.
- Features Are Not Working as Expected.
- Fix: This could be a misconfiguration. Look for a “reset to default settings” option within the software’s preferences. Alternatively, it could be a known bug that is addressed in a recent update.
- Files Aren’t Saving Correctly.
- Fix: Check if you have adequate disk space. Then, verify you have the correct permissions to save to the chosen folder. Try saving the file to a different location, like your desktop.
- Software Won’t Update.
- Fix: A weak internet connection or firewall can block updates. Ensure you’re connected to the internet and check your firewall settings to make sure it isn’t blocking the application’s connection.
- Compatibility Issues with the Operating System.
- Fix: Many operating systems have a compatibility mode. On Windows, you can right-click the application’s icon, go to Properties > Compatibility, and run it in a mode for an older version of Windows.
- The Program Looks Distorted or Displays Incorrectly.
- Fix: This is almost always a graphics driver issue. Visit the website for your graphics card manufacturer (like NVIDIA, AMD, or Intel) and install the latest drivers.
- Your License or Activation Key isn’t Working.
- Fix: Double-check that you entered the key correctly. Many activation issues are also tied to the system’s date and time being incorrect, so ensure it’s synced properly. (Read our guide on how to check if Windows is activated.)
- You Suspect Malware is Causing the Problem.
- Fix: If the software is behaving erratically or you see lots of pop-ups, run a full system scan with reputable antivirus and anti-malware software.
Did you know? Windows has free built-in Antivirus called “Windows Defender” / “Windows Security“. Read our guide here on how to activate Windows Security and run antivirus full scan on your system.
- The Software Can’t Find a Connected Device (like a printer).
- Fix: Check the physical connection and ensure the device is powered on. Next, reinstall the drivers for the device. A missing or corrupt driver is the most common cause.
Did you know? If you are using Windows, there are multiple ways to get help in Windows (from built-in features to get Microsoft Support. Read our comprehensive article on how to get help in Windows.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques for Tough Problems
If you’ve tried the common fixes and the problem persists, it’s time to use some more powerful techniques.
- Boot into Safe Mode: Starting your computer in Safe Mode loads only the essential system files and drivers. If the software works correctly in Safe Mode, it strongly suggests a conflict with another program or driver that loads during a normal startup.
- Perform a Clean Boot: This is a more targeted step than Safe Mode. A Clean Boot starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and startup programs, but it gives you control to systematically re-enable services to pinpoint the exact one causing the conflict. It is the perfect tool for isolating a background service conflict.
- Check System Logs with Event Viewer: On Windows, the Event Viewer records important events, including application errors. Look for red critical error icons that occurred at the same time your software crashed. The details in these logs can provide technical clues that point directly to the root cause.
- Run the System File Checker (SFC): Corrupted operating system files can cause widespread software instability. The SFC tool (run by typing sfc /scannow in an administrative Command Prompt) scans and repairs protected system files. For more information, see the official Microsoft documentation on the SFC tool.
Helpful Tools for Software Troubleshooting
While your logic is your best tool, several utilities can make the process much easier.
- Built-in OS Tools:
- Task Manager / Activity Monitor: Essential for identifying resource-hungry processes.
- Event Viewer / Console: Provide detailed error logs for deep analysis.
- Resource Monitor: Gives a more detailed view of CPU, memory, disk, and network usage than Task Manager.
- Third-Party Utility Software:
- Advanced Uninstaller Tools: Programs like Revo Uninstaller can remove all leftover files and registry entries that a standard uninstall might miss.
- System Cleaner Applications: Reputable tools can help clear out temporary files, fix registry issues, and manage startup programs.
- Malware Scanners: A good second-opinion scanner like Malwarebytes can catch threats that a primary antivirus might miss.
Best Practices for Preventing Software Problems
The best way to fix a problem is to prevent it from ever happening.
- Keep Everything Updated: Regularly update your operating system, drivers, and applications.
- Understand System Requirements: Before installing new software, always check that your computer can handle it.
- Use Reputable Antivirus/Antimalware: Protect your system from malicious software that can cause widespread issues.
- Perform Regular Maintenance: Use built-in tools like Disk Cleanup on Windows to remove temporary files that can bog down your system. For more technical guidance, you can review resources like the Microsoft Support lifecycle FAQ.
When to Stop: Knowing When to Call for Professional Help
Sometimes, a problem is too complex or risky to solve on your own. You should consider stopping and seeking help from the software’s official customer support or a local IT professional if:
- You’ve spent several hours on the problem with no progress.
- The proposed solutions involve editing the Windows Registry or other critical system settings you are not comfortable with.
- You suspect the issue is hardware-related.
- The problem involves critical business data that could be lost.
Knowing your limits is a key part of effective troubleshooting.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How do I troubleshoot an unknown error?
A: If you get an error message with no clear meaning, the first and most important step is to type the entire error message into a search engine like Google or Bing. You are likely not the first person to see it, and the solution is often in a support forum or technical blog post.
Q: What is the very first step in troubleshooting?
A: The absolute first step is to clearly identify and understand the problem. Before you change anything, you must know what is happening, when it happens, and what the specific symptoms are. This prevents you from making the problem worse.
Q: How can I tell if it’s a software or hardware issue?
A: A good rule of thumb is to see if the problem is isolated. If only one program crashes, it’s likely a software issue. If multiple programs are crashing, or if you’re seeing issues like the “Blue Screen of Death,” it could point to a hardware problem with your RAM or hard drive.
Conclusion: You Are Now the Troubleshooter
Troubleshooting software doesn’t have to be a daunting task. By moving away from random clicking and adopting a structured, step-by-step methodology, you can solve problems faster and more effectively.
Start with the quick fixes, but don’t be afraid to use the 7-step process for tougher issues. You now have the framework to confidently diagnose and fix nearly any software issue that comes your way.
If this guide on “how to troubleshoot software issues” helped you, please consider sharing it with others! What are your go-to troubleshooting tricks? Let us know in the comments below.
IT Security / Cyber Security Experts.
Technology Enthusiasm.
Love to read, test and write about IT, Cyber Security and Technology.
The Geek coming from the things I love and how I look.

