In this article, I will show you how to use Powershell to check if file exists.
There are two options on how to achieve it by using either command:
- Test-Path
- [System.IO.File]::Exists($path)
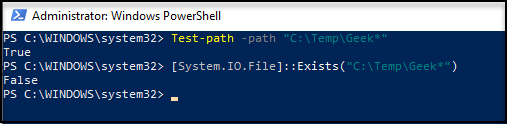
The difference between two options is Test-Path supported using wildcards, while the other options do not.
You either can directly run a standalone command or using if-else for both options.
If using standalone command, you can run directly from Powershell console. If you want to use if-else, it is best recommend to use “Powershell ISE”.
The differences between both standalone and if-else are, standalone is sufficient if you only want to know if the file is exists or not. Use if-else if there is further action will be proceed, depends on the status of the file; found or not.
Standalone command will return as “True”, means the file is exists. If it returns “False” means it does not exists. While using if-else will not return any True or False or any output. Output will be depends on what user wants to output based on the conditional set.
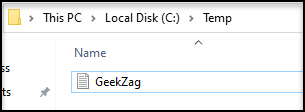
Before start, as I example, I need to create the sample file. Let’s says on “C:\Temp\Geekzag.txt”
A. Using Test-Path
1. Powershell Check If File Exists Without Variable
The command to check the file is exists:
Test-Path -path $path
Where $path is the location of the file.
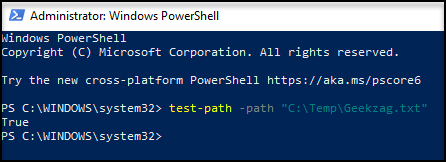
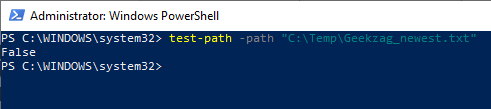
Here is example to run a standalone command for both if found or not:
Here is example to run using if-else with action:
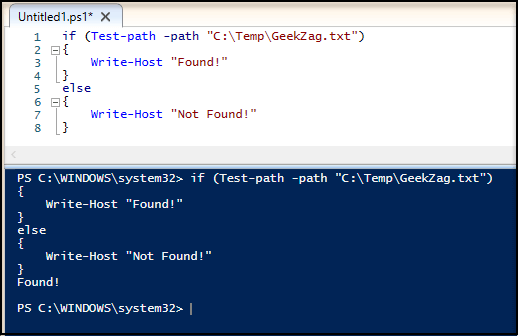
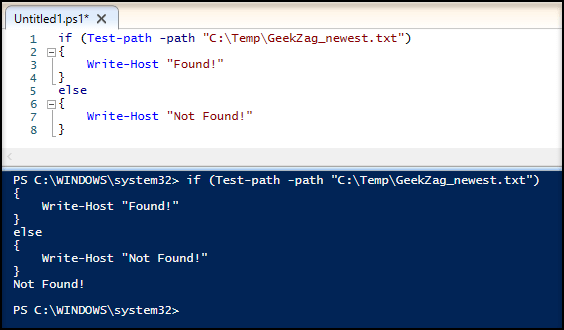
Since I set a status string as the output, it will output either Found or Not Found.
Here is example to run using if-else with without action:
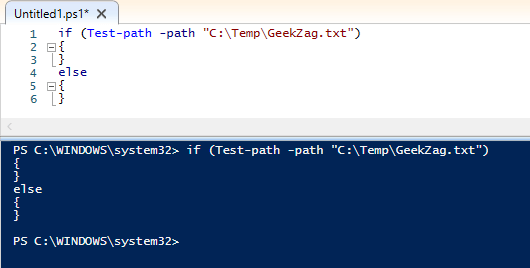
As you can see, it does not out put any results.
2. Powershell Check If File Exists With Variable
The command is the same as previously using Test-path. But, in this example, I will assign the command into variable, then run the variable as commands or use the variable as a statement conditional in if-else.
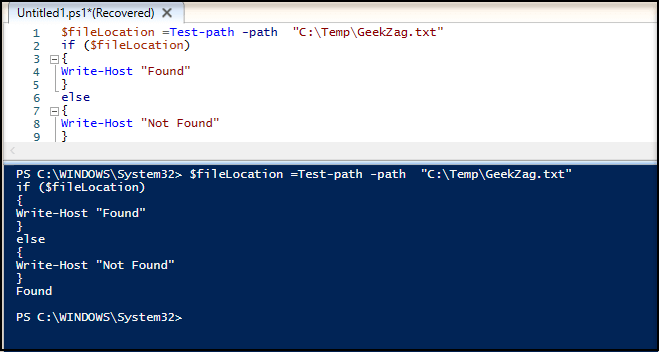
Here is example to run a standalone command for both if found or not:
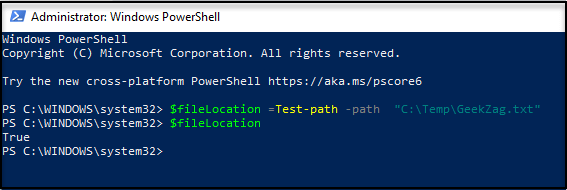
Here is example to run using if-else with action:
B. Using [System.IO.File]::Exists($path)
1. Powershell Check If File Exists Without Variable
The command to check the file is exists:
[System.IO.File]::Exists($path)
Where $path is the location of the file.
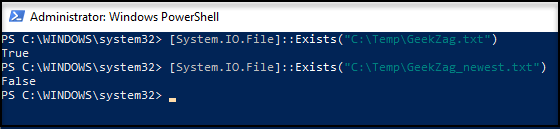
Here is example to run a standalone command for both if found or not:
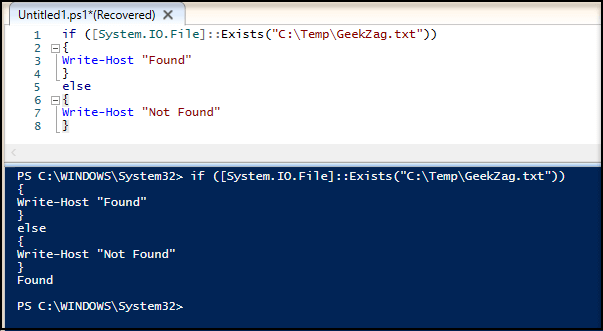
Here is example to run using if-else with action:
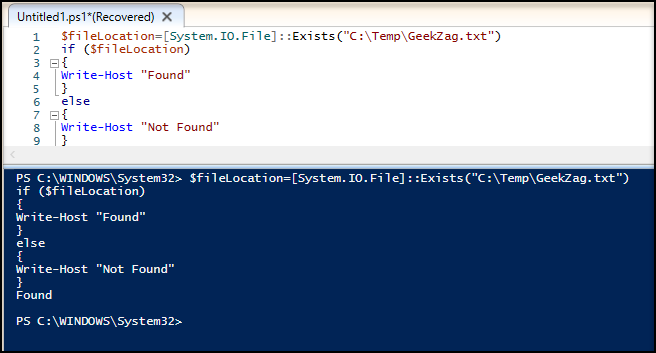
2. Powershell Check If File Exists With Variable
The command is the same as previously . But, in this example, I will assign the command into variable, then run the variable as commands or use the variable as a statement conditional in if-else.
Here is example to run a standalone command for both if found or not:
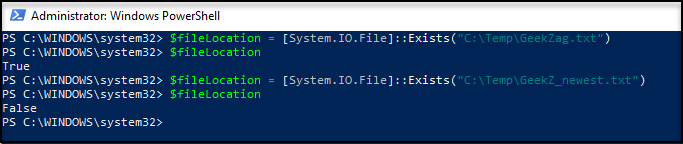
Here is example to run using if-else with action:
Difference Between Two Options
As mentioned earlier, Test-path support wildcards while the other does not:
Conclusions
Both options provide the same output on checking if file is exists. However, I personally prefer to use “Test-path” as the command is easy to remember and support wildcards.
Thanks for reading this article. I hope you find it helpful.